The concept of L1 L2 and L3 cache memory is really interesting.
When we check the processor of a laptop, there are some terms named like L1, L2, and L3 cache.
Most people ignore this part because they aren’t aware of it.
Should you also ignore it?
Well…no you should not.
It is an important part of a CPU and plays a vital role in speed.
So what is L1 L2 and L3 cache in the processor? Let’s find it out.
What is L1, L2 and L3 Cache?
For easy understanding, the L stands for Level.
So L1, L2, and L3 are basically three levels of cache.
To understand the concept of L1, L2, and L3 cache, you must have an idea about the CPU cache.
What is Cache memory?
For those who don’t know, there are two types of RAM.
- DRAM (Dynamic RAM)
- SRAM (Static RAM)
DRAM is the memory that uses capacitors to store the data. These capacitors have to constantly and dynamically be refreshed often with electricity in order to store the data.
SRAM is a memory that doesn’t have to be constantly refreshed. Because of it, the SRAM is a lot faster than DRAM, and also very expensive.
SRAM is what is used in the CPU cache.
The CPU cache is CPU’s internal memory. Its job is to copy and store the data and instructions from RAM that is waiting to be used by the CPU.
Basically what the CPU cache does is that it hold common data that it thinks the CPU is going to access over and over again.
When the CPU needs the data, it always checks the faster cache memory first.
If the data isn’t there, then CPU has to go to the slower primary memory which is RAM or DRAM.
That’s why cache memory is so important.
If you are interested, then check these Best Laptop For IT Professionals.
What is L1 Cache?
The primary memory in the CPU or processor is Level 1 or L1 cache.
The L1 memory is located on the processor itself so it runs at the same speed as the processor. It’s the fastest cache on the laptop or computer.
What is L2 Cache?
The L2 or Level 2 cache is an external cache that is not located on the CPU itself.
The L2 cache is used to catch recent data accesses from the processor that were not caught by the Level 1 cache.
In simple words, If a CPU can’t find the data it needs in the L1 cache, it then searches the L2 cache for the data.
If the CPU can’t find the data in the L2 cache, then it searches the last level of cache which is Level 3 cache.
What is L3 Cache?
The L3 or Level 3 cache is the last level of CPU cache which is used to catch recent data accesses from the processor that was not caught by the Level 2 cache.
And finally, if the CPU doesn’t find the data in the L3 cache, then the CPU has to go back to the slower RAM.
How does L1, L2 and L3 cache memory help a CPU?
The whole idea behind the L1, L2, and L3 cache is to make a laptop or computer as fast as possible.
Because the L1 cache is located on the CPU itself, it’s the fastest among all.
But,
In the upcoming generation of processors, the L2 and L3 cache will also be located on the CPU itself to make the whole processing a lot faster.
Now coming to the point, how do L1, L2, and L3 cache memory help a CPU?
Even though the RAM has become a lot faster, it still can’t feed the data to the CPU fast enough.
The CPU has become so fast that a lot of time the CPU does nothing and keeps waiting around for more data to process.
It’s like wasting the true power of the CPU because of slow RAM.
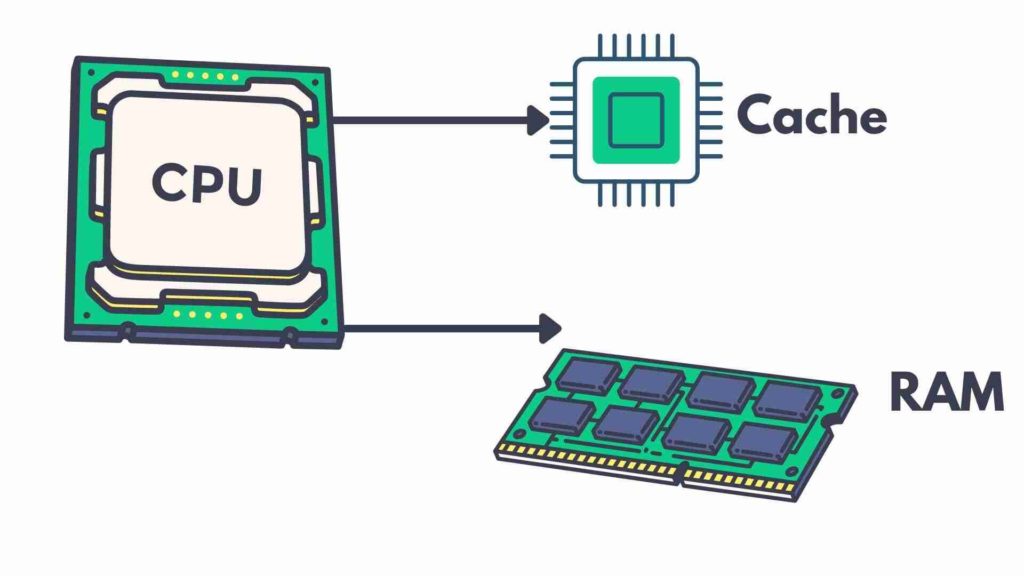
That’s where the cache memory came into existence to solve this problem.
The cache memory acts as a middle man between CPU and RAM to assist and feed a CPU the data it needs a lot faster.
What is a good cache size?
The more you pay, the more you get.
If you look at the cheap laptops, you will find that most CPUs have an L1 cache of 192KB to 348KB.
Especially the Intel or Ryzen 3 laptops under 30k have:
- L1 cache: 192KB to 348KB
- L2 cache: 1 MB
- L3 cache: 4MB
So this is the base cache storage. Generally, companies only advertise the L3 cache because it’s the biggest cache among all but not the fastest one.
If you pay more, the size of cache memory increases accordingly.
For example. The laptops with Intel i5 10th gen processor have 6MB of cache.
So basically, the size of cache memory depends on the processor you choose.
If you want more cache memory, you have to pay more.
FAQs
Can CPU run without cache memory?
Yes, a CPU can run without the cache memory, but the speed would be so slow that it can take hours to perform a few operations.
That’s why companies have integrated cache like L1 cache so that you would never have to deal with such a slow speed.
Why is L1 cache so small?
The simplest reason for the L1 cache being so small is the speed and cost.
Because the L1 cache is so fast, it can process the data in milliseconds.
Another reason is cost. The speed of the L1 cache has to match up with the CPU’s speed, which results in higher costs.
So there is no need to make a 5-10MB L1 cache because it will exponentially increase the cost.
Which is better L1 L2 or L3 cache?
All the L1, L2, and L3 cache are important.
L1 is the fastest, but smallest. L2 sits right in the middle in both the speed and storage. L3 is the biggest but slowest among the three.
For speed:
L1>L2>L3
For storage:
L3>L2>L1
So this is what the L1 L2 and L3 cache is used for.
If you still have any doubt, then feel free to ask us in the comment sections.
Also, check these Amazingly Best Boat Rockerz in India.
Now, we hope you have a better idea about the L1, L2, and L3 cache.
If you have found this information helpful, then consider sharing it with others.






